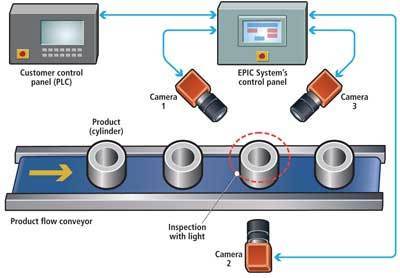
Machine Vision (MV) is industry application-oriented subset of computer vision. It is the study of methods and techniques whereby artificial vision systems can be constructed and usefully employed in manufacturing applications. Machine vision integrates image capture systems with digital input/output devices and computer networks to provide real time quality control and for general control of manufacturing equipment such as automated assembly systems and robotic manipulator. Manufacturers accept machine vision systems due to its high-speed,
high- magnification, 24-hour operation, and/or repeatability of measurements for visual inspection applications.
Machine Vision (MV) systems can be applied in almost any industry. Historically the first systems were deployed in the semi-conductor and automotive industries due to their highly intensive use of industrial automation within these industries. Modern vision systems can be applied across a hugely diverse range of industry sectors, these industries include: Automotive, Semi-conductor, Electronics, Medical Devices and Pharmaceutical, Printing and Packaging, Food Processing, Solar Production and Process Engineering.
high- magnification, 24-hour operation, and/or repeatability of measurements for visual inspection applications.
Machine Vision (MV) systems can be applied in almost any industry. Historically the first systems were deployed in the semi-conductor and automotive industries due to their highly intensive use of industrial automation within these industries. Modern vision systems can be applied across a hugely diverse range of industry sectors, these industries include: Automotive, Semi-conductor, Electronics, Medical Devices and Pharmaceutical, Printing and Packaging, Food Processing, Solar Production and Process Engineering.
- Teacher: S.A.R. Sheik Masthan